What Is Deep Learning (DL)?
Deep Learning is a more advanced subset of machine learning. It relies on artificial neural networks—complex architectures inspired by the structure of the human brain. These networks consist of multiple layers that can learn increasingly abstract representations of data.
DL has gained momentum due to the rise of big data and improvements in computing power, especially GPUs. It is now used in highly complex tasks where traditional ML falls short. For example, DL powers self-driving car systems like Tesla’s Autopilot, helps analyze medical imaging to detect tumors, and enables voice assistants like Siri to understand natural language.
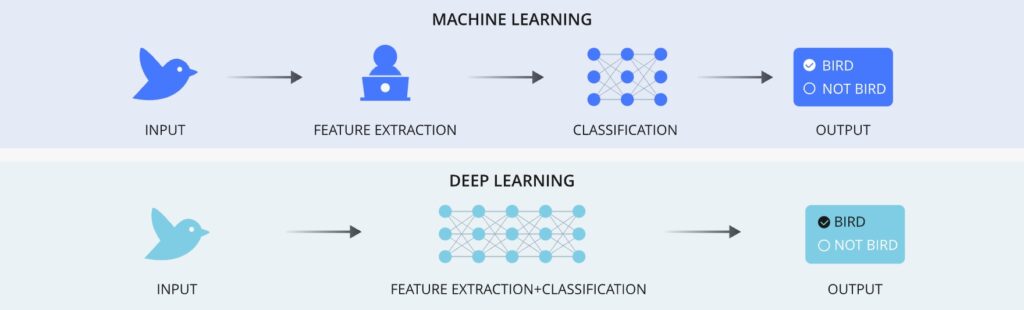
Unlike traditional ML, which often requires manual feature extraction, DL can automatically identify relevant features from raw data, which makes it particularly powerful in fields such as image recognition and natural language processing.
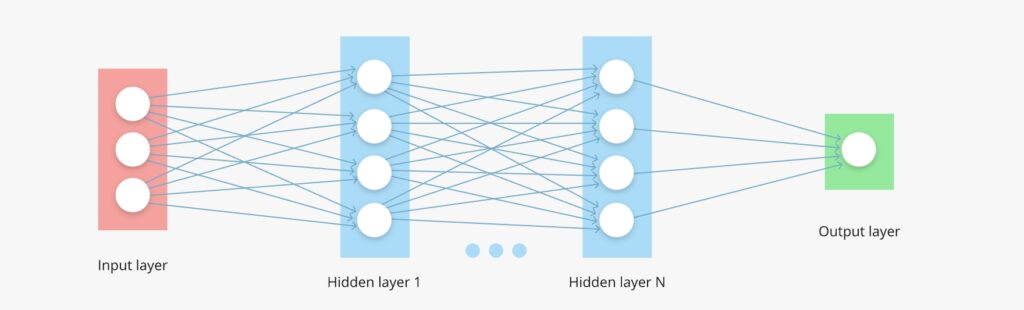
Types of Deep Learning Layers:
The input layer of nodes receives the information and transfers it to the underlying nodes;here the network fixates on patterns of local contrast as important.
Hidden node layers are the ones where the computations appear, this is the layer that uses those patterns of local contrast to fixate on things that resemble
In the output node layer, the results of the computations will show up. In this layer, the features will be applied to templates.