What Is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning is a specialized branch within the broader field of AI. It focuses on enabling systems to automatically learn and improve from experience, rather than being explicitly programmed. This means that instead of writing code to solve every problem, developers train models with data, allowing machines to identify patterns and make predictions.
There are three main types of ML:
Supervised learning
, where models are trained on labeled data (e.g., email spam filters).
Unsupervised learning
, where systems identify patterns without labeled outputs (e.g., customer segmentation).
Reinforcement learning
, which involves decision-making through trial and error (e.g., AI that learns to play video games).
Common ML applications include email filtering in Gmail, personalized product recommendations on Amazon, and predictive maintenance in manufacturing facilities. Many of these use cases now power critical business operations and digital services we use every day.
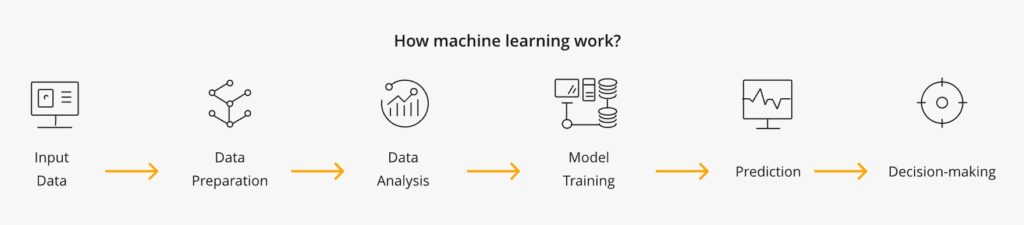
How Does Machine Learning Work?
Input Data: The process begins by collecting different types of data—text, images, sound files, or numerical values—that represent the real-world problem being addressed.
Data Preparation: This data is cleaned and formatted to improve quality. Inconsistencies and missing values are corrected to ensure the model learns from reliable input.
Exploratory Analysis: The algorithm examines the data to identify relationships between features and understand underlying trends.
Pattern Identification: Based on what it learns, the model starts recognizing consistent patterns that influence outcomes.
Prediction: Using the patterns it has learned, the model applies this knowledge to new data to make predictions or classifications.
Decision-Making: These predictions guide decisions or actions—such as filtering an email into a spam folder or recommending a product on an e-commerce site.