
George May 23, 2025
With the rapid boom of artificial intelligence in 2025, terms like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Generative AI (GenAI) are appearing everywhere—from enterprise software to everyday mobile apps. However, despite their widespread use, many people still struggle to distinguish between them. Are they just different names for the same thing? Or are there key differences?
Understanding these distinctions is critical, whether you’re adopting AI-driven tools at work, reskilling for the digital economy, or simply trying to keep up with tech conversations. In this guide, we break down the definitions, use cases, and core differences between AI, ML, DL, and GenAI. You’ll also explore a helpful comparison table and real-world applications across industries.
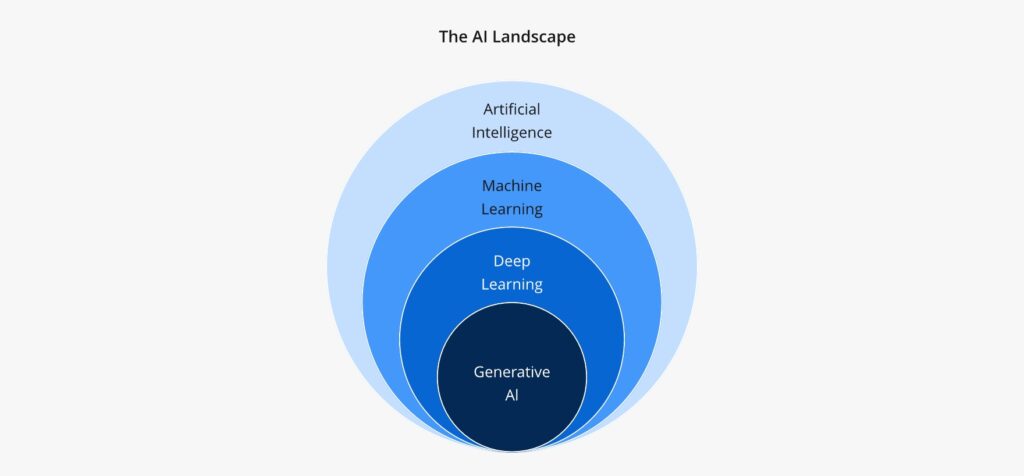
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, refers to the broad concept of machines or software mimicking human intelligence. This includes learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making. The term was coined in 1956, and since then, AI has evolved to become an umbrella term covering everything from rule-based systems to advanced neural networks.
At its core, AI seeks to replicate tasks that typically require human intelligence. This can include recognizing speech, making decisions, interpreting data, and even understanding language. Today, AI is used in diverse applications such as customer support chatbots, fraud detection systems in banking, and supply chain optimization engines.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
AI can be categorized into three main types:
Narrow AI (Weak AI): Focused on specific tasks and domains, such as facial recognition or recommendation systems. Most AI applications today fall into this category.
General AI (Strong AI): A theoretical form of AI that can perform any intellectual task a human can do. It remains a long-term goal in the AI community.
Superintelligent AI: A hypothetical AI that surpasses human intelligence across all domains. This form of AI is the subject of much philosophical and ethical debate.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Today, AI is used in diverse applications across industries, these use cases reflect AI’s growing influence on both business and everyday life.
Customer support chatbots that handle common inquiries
Fraud detection systems that flag suspicious financial transactions
Supply chain optimization engines that predict demand and streamline logistics
Voice assistants like Siri and Alexa that respond to voice commands
Smart home systems that automate lighting, temperature, and security